What is a soft tissue injury?
Soft tissue injuries (STI) are when trauma or overuse occurs to muscles, tendons or ligaments. Most soft tissue injuries are the result of a sudden unexpected or uncontrolled movement like stepping awkwardly off a curb and rolling over your ankle. These are injuries our Physiotherapists see every day at our Edinburgh physiotherapy and sports injury clinics. However, soft tissue damage can also occur from excessive overuse or chronically fatigued structures, especially muscles and tendons. For example, if you were to do a long run when already fatigued (from a previous run or exercise), then it is possible to cause trauma or a strain to key running musculoskeletal structures like your calf muscles or achilles tendons, also see: “How to prevent running injuries”.
What are the most common soft tissue injuries?
- Ankle Spain
- Back Strain (see article on back pain)
- Calf Strain
- Golfers/Tennis elbow
- Hamstring strain
What is the difference between a strain and a sprain?
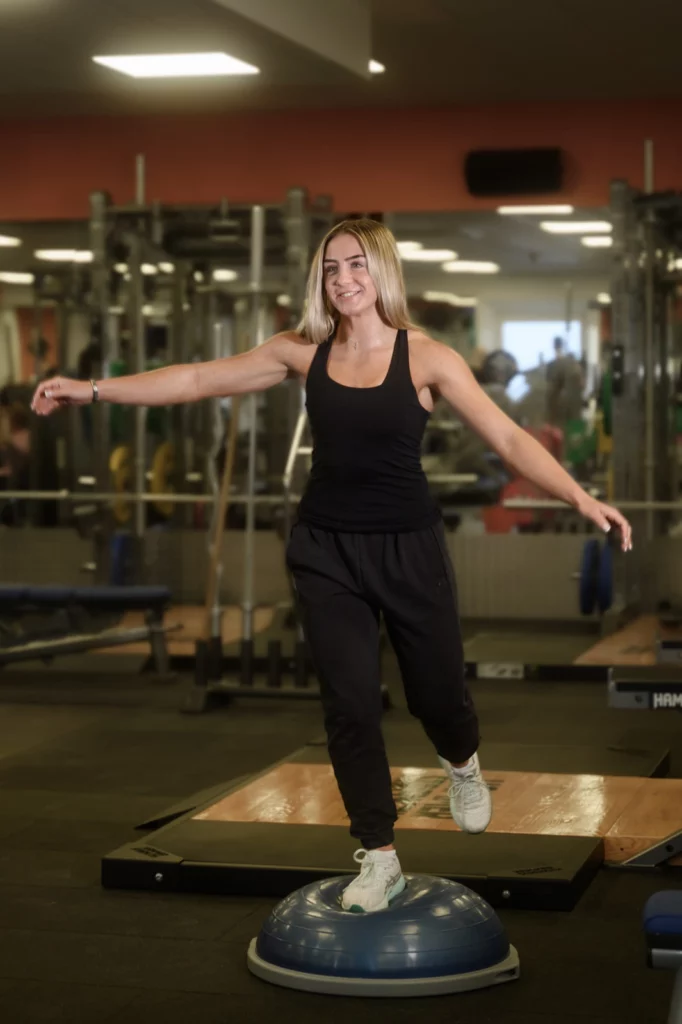

Grade 1 strain or sprain (mild)
- Minimal over-stretching. Possible minor microscopic tearing of fibres
- Mild tenderness and minimal swelling
Grade 2 strain or sprain (moderate)
- Partial tear of fibres
- Moderate pain, tenderness and swelling
- Unable to apply loading to injured area without pain
Grade 3 strain or sprain (severe)
- Complete rupture of structure
- Significant pain and swelling
- Inability to use the injured structure
- Instability of the affected joint
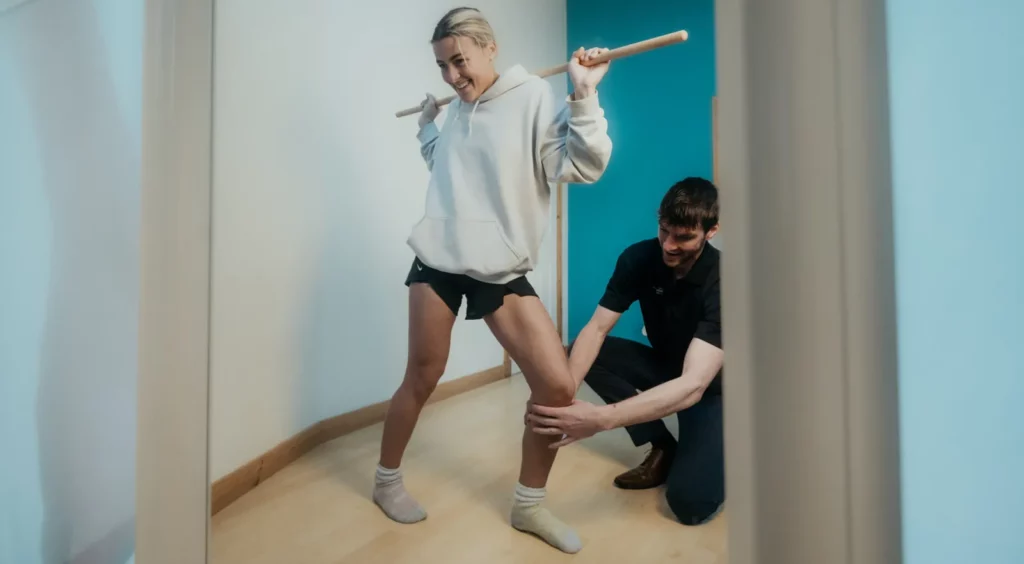

What are the symptoms of soft tissue injuries?
How long will it take to recover from a soft tissue injury?
Treatment for soft tissue injuries:
Stage two: Reduce swelling and stiffness and begin to regain normal movement.
Stage three: Regaining of normal function and return to normal activities.
Should I go to a hospital with a soft tissue injury?
- You are unable to put any weight on the injured structure
- There is an unusual deformity or shape
- You heard a pop or crack at the time of injury
- Any surrounding bony structures are painful
- There is presence of neurological signs like numbness or pins and needles (either at the injury site or anywhere else)
PRICE Regime for Soft Tissue Injuries
Protect
Rest
Ice
Compression
Elevation
What to avoid when you have a soft tissue injury?
Heat
Alcohol
Massage
Physiotherapy treatment for soft tissue injuries
An experienced Physiotherapist can assess your injury, and confirm both the diagnosis and extent of damage. They will provide you with advice, hands-on treatment and exercises which will promote a prompt and effective recovery, as well as reduce the risk of further injury in the future. (see also “how to avoid running injuries”) Your Specialist Physiotherapist will also advise you on a progressive return to normal activities and alternative exercises to follow whilst you are injured.
What Exercises are there for Soft Tissue Injuries?

Initial Post Ankle Injury Exercise

Regaining Balance After an Ankle Injury

Ankle Strengthening
Find a location near you
The Physiotherapy Clinics - Gracemount
The Physiotherapy Clinics - Leith
The Physiotherapy Clinics - South Gyle
Peebles Physiotherapy
The Physiotherapy Clinics - Fairmilehead
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I can't thank Peter enough for guiding me through my shoulder rehabilitation program over the past few months. His instructions were very clear and the instructional videos made available through the app were really useful. I'd had niggling, low-level pain in my shoulder for around 13 years and then recently I lost full range of motion due to a karate injury; after working with Peter I can honestly say that my shoulder now feels better and stronger than it has done for a very long time! Thanks again :-)Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very grateful. Great serviceTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I received fantastic, friendly help from Biju for a minor leg injury. The treatment and exercises he gave me completely sorted my issue. Would 100% recommend both him and the clinic!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Had a great experience at this clinic. Antony put together a detailed treatment plan for treating knee pain. He clearly explained how each exercise would benefit the activities I wanted to be able to do. Not only is he a great physio, but he is so friendly and always makes you feel listened to.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Phil has been supporting me a long standing complicated issue, which previous places have been unable to help. Phil's extensive experience and positive approach, coupled with his willingness to think outside the box is making a difference. Recently this approach has included the 3D movement scan. It's very easy to participate in, and it revealed problematic postural and movement detail that would be harder to discover by other means. I recommend the 3D scan as a rehabilitation tool.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I highly recommend the physiotherapy clinic South Gyle. I received a detailed assessment of my problem from Phil. He clearly explained the issues I'm having and why, plus the treatment, exercises required to rectify. Really happy with my experience and I would not hesitate to go back. Thanks PhilTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I first attended the South Gyle clinic to see Anthony Guiducci on February 2023. I was suffering from a very painful trapped nerve in the lower back. Later in the year, with the back issue having been virtually cleared, I developed some nerve pain in the right knee along with general stiffness in the left knee. Finally around late October I had "tennis elbow" on my right elbow.I should say that I am 73 years old and spent many years playing contact sports, mainly rugby and football and now in my twilight years golf. It catches up with you eventually 😁. All through this time Anthony has been totally professional with a great knowledge of muscle and nerve structure and their interaction. His approach to giving you remedial exercises is well structured to your ability and takes great care that you keep within your capabilities as you build up the strengthening and more testing lessons. I can highly recommend him to anyone looking for physio help with their injuries or aches and pains. I must also say that, on the odd occasion when I had to use other physios at South Gyle, due to holiday leave I was equally impressed by the expertise of the staff.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Came here with a mild hamstring strain, ran a 3:30 marathon 5 weeks later! Anthony Guiducci = legendTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Really thorough consultation. Excellent advice and follow-up arranged.